
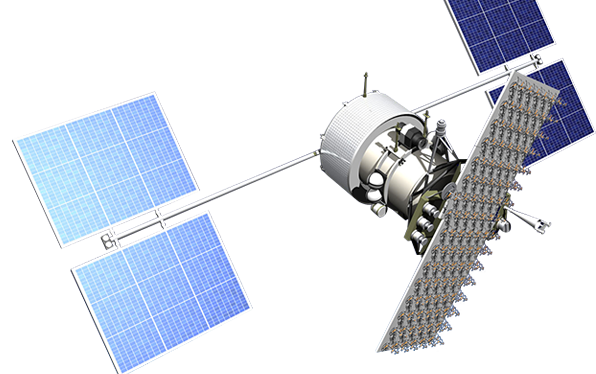
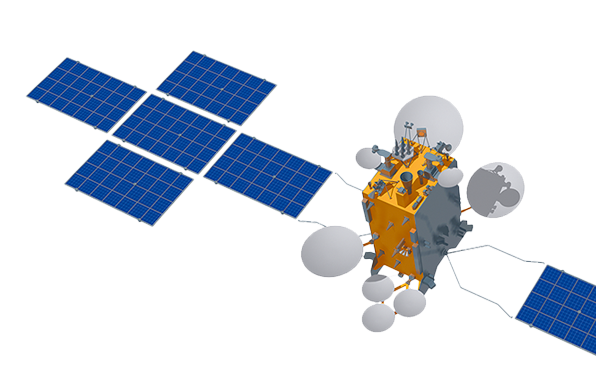
The Russian Satellite Communications Company (RSCC) is the Russian satellite operator whose spacecraft provide a global coverage. RSCC belongs to the ten largest world GEO satellite operators in terms of satellites and orbital slots and has 57 years of experience. RSCC provides a full range of communications and broadcasting services via its own satellite fleet of 12 satellites and terrestrial infrastructure: video distribution and contributions, DTH services, satellite news gathering, presidential and government applications, broadband access and Internet, IP trunking and cellular backhaul, mobility solutions for vessels and other. The company deploys regional TV satellite distribution networks as well as multi-functional corporate and government VSAT networks. Today RSCC is present at all geographically available markets, providing services for customers from more than 60 countries worldwide.
The company possesses the largest satellite constellation in Russia located in the geostationary orbital arc from 14 West to 145 East and cover the whole territory of Russia, the CIS, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Asia Pacific region, North and South America, and Australia. RSCC includes six teleports - Satellite Communications Centers (SCC): Dubna, Bear Lakes, Skolkovo, Zheleznogorsk, Khabarovsk, Vladimir and the Shabolovka Technical Center in Moscow as well as its own high-speed optical-fiber digital network.
































































![681485 [hWwzps]](/media/images/681485_hWwzps_mIwXnzN.2e16d0ba.fill-640x400.png)
